How to Increase VO2 Max: Techniques to Improve Performance
VO₂ max, the key indicator of aerobic fitness, measures the body’s maximum oxygen uptake during exercise. This article delves into the science behind VO₂ max, its role in athletic performance, and effective strategies to improve it. Covering training techniques, nutrition, recovery, and health benefits, it provides a comprehensive guide for athletes and fitness enthusiasts aiming to optimize endurance and overall well-being.

Understanding VO₂ Max
VO₂ max, or maximal oxygen uptake, is the gold standard for measuring cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. It represents the maximum amount of oxygen your body can utilize during intense exercise. Athletes and fitness enthusiasts strive to improve their VO₂ max to enhance endurance, performance, and overall health.
The Science Behind VO₂ Max
VO₂ max is expressed in milliliters of oxygen per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). The higher the value, the more efficiently an individual can transport and use oxygen. This efficiency directly impacts stamina and athletic performance.
Several physiological factors influence VO₂ max:
- Cardiac output: The heart’s ability to pump blood.
- Pulmonary function: Lung capacity and oxygen exchange efficiency.
- Muscle oxygen extraction: The muscles’ ability to absorb and utilize oxygen.
Training, genetics, and age all play roles in determining an individual’s VO₂ max. While some elite athletes have naturally high levels, strategic training can enhance it significantly.
Importance of VO₂ Max for Athletes
Performance Enhancement
A high VO₂ max allows athletes to sustain high-intensity efforts for longer periods. It enhances endurance sports like running, cycling, and swimming. Increased oxygen uptake means muscles receive more fuel, delaying fatigue and improving efficiency.
Recovery and Adaptation
Improved VO₂ max facilitates faster recovery. Oxygen-rich blood clears metabolic waste like lactate more efficiently, reducing soreness and improving readiness for the next workout.
Methods to Measure VO₂ Max
Laboratory Testing
The most accurate method is a graded exercise test (GXT) performed in a lab. This test involves running or cycling while oxygen consumption is measured via a metabolic cart. The test continues until exhaustion, providing an exact VO₂ max value.
Field Tests
For those without access to lab testing, field tests offer a practical alternative. These include the Cooper test (12-minute run), the beep test, and submaximal exercise tests. Though less precise, they provide useful estimations for tracking improvements.
Training Strategies to Improve VO₂ Max
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
HIIT is one of the most effective ways to boost VO₂ max. Short bursts of intense effort followed by recovery periods push the cardiovascular system to adapt.
Benefits of HIIT for VO₂ Max
- Rapid improvements in aerobic capacity.
- Increased stroke volume of the heart.
- Enhanced mitochondrial density in muscles.
Continuous Endurance Training
Long-distance running, cycling, or swimming at a moderate intensity gradually improves VO₂ max. In addition, this method strengthens the heart while also increasing capillary density. As a result, oxygen delivery to muscles becomes more efficient, ultimately boosting endurance and performance. Therefore, incorporating these activities into a routine can significantly enhance cardiovascular fitness over time.
Strength Training and VO₂ Max
Although strength training is traditionally not associated with aerobic capacity, it still plays a role in improving VO₂ max. In fact, stronger muscles utilize oxygen more efficiently, which in turn enhances endurance performance. Therefore, incorporating strength training into a workout routine can significantly boost overall cardiovascular fitness and stamina.
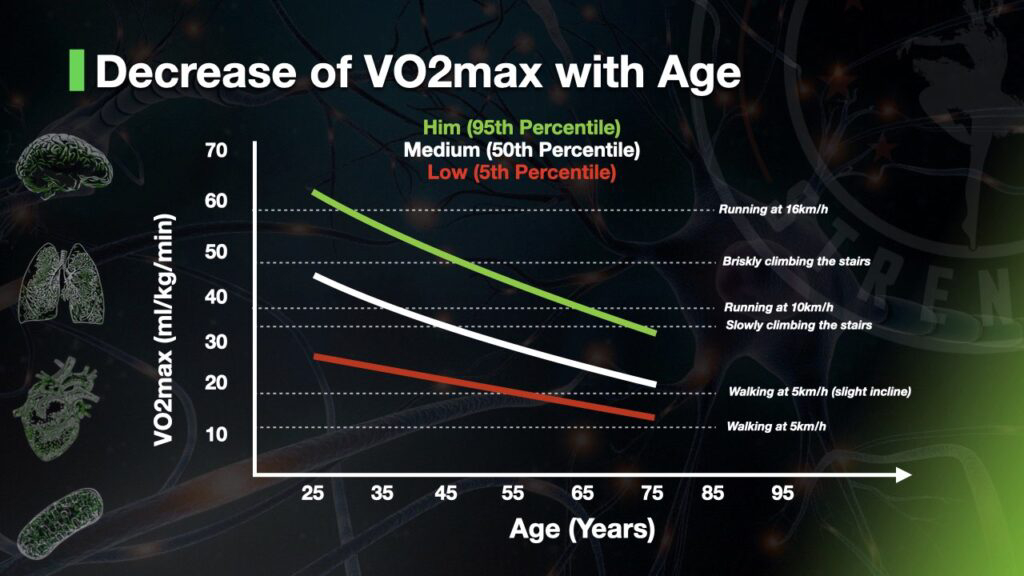
Factors Affecting VO₂ Max
Genetics and Age
Some individuals naturally have a higher VO₂ max due to genetic factors. Additionally, age influences VO₂ max, as it tends to decline over time. However, consistent training can effectively slow down this decline. Therefore, maintaining a regular exercise routine is essential for optimizing VO₂ max and supporting overall cardiovascular fitness.
Altitude and Environmental Conditions
Training at high altitudes naturally increases red blood cell production, which in turn improves oxygen transport. Additionally, factors such as temperature, humidity, and pollution levels significantly impact athletic performance. Moreover, these environmental conditions influence VO₂ max testing, ultimately affecting endurance and overall fitness levels. Thus, adapting to such variables is essential for optimizing performance.
Nutrition’s Role in VO₂ Max
Oxygen Utilization and Fuel Sources
A balanced diet supports cardiovascular function and oxygen utilization. Key nutrients include:
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport in the blood.
- Nitrates: Found in beets, improving blood flow and oxygen efficiency.
- Carbohydrates: Primary fuel source for high-intensity activities.
Hydration and Performance
Dehydration reduces blood volume, making oxygen transport less efficient. Maintaining adequate hydration optimizes VO₂ max performance during exercise.
The Role of Recovery in VO₂ Max Improvement
Sleep and Oxygen Utilization
Quality sleep is essential for cardiovascular recovery because it allows the body to heal and regenerate. Additionally, the release of growth hormone during sleep helps with muscle repair while also enhancing aerobic capacity. As a result, getting enough rest not only supports heart health but also improves overall physical performance and endurance.
Active Recovery Methods
Incorporating light exercises, such as swimming or yoga, helps promote circulation, which in turn reduces muscle stiffness while also aiding VO₂ max gains. Additionally, these activities enhance flexibility and support overall cardiovascular health. By making them a regular part of your routine, you can improve endurance and optimize oxygen utilization for better performance.
VO₂ Max and Longevity
Higher VO₂ max levels are directly linked to a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases. Furthermore, maintaining a strong aerobic capacity not only boosts heart health but also enhances overall longevity and quality of life. Therefore, incorporating regular aerobic exercise can significantly contribute to long-term well-being and a healthier lifestyle.
VO₂ Max as a Health Indicator
Studies show that individuals with higher VO₂ max levels tend to experience lower mortality rates. In fact, VO₂ max serves as a key predictor of cardiovascular health as well as metabolic function. Therefore, improving aerobic capacity can significantly enhance overall well-being and longevity. By focusing on endurance training, individuals may effectively boost their VO₂ max levels.
Our bodies are our gardens – our wills are our gardeners.
WILLIAM SHAKESPEARE
Conclusion
VO₂ max is a crucial factor in athletic performance, endurance, and overall health. Understanding its science, training strategies, and contributing factors can help athletes maximize their potential. Through targeted training, proper nutrition, and recovery strategies, individuals can enhance their VO₂ max and achieve peak performance.